farmbot开发入门教程-点群排序
说明:
- 介绍点群排序的工作原理
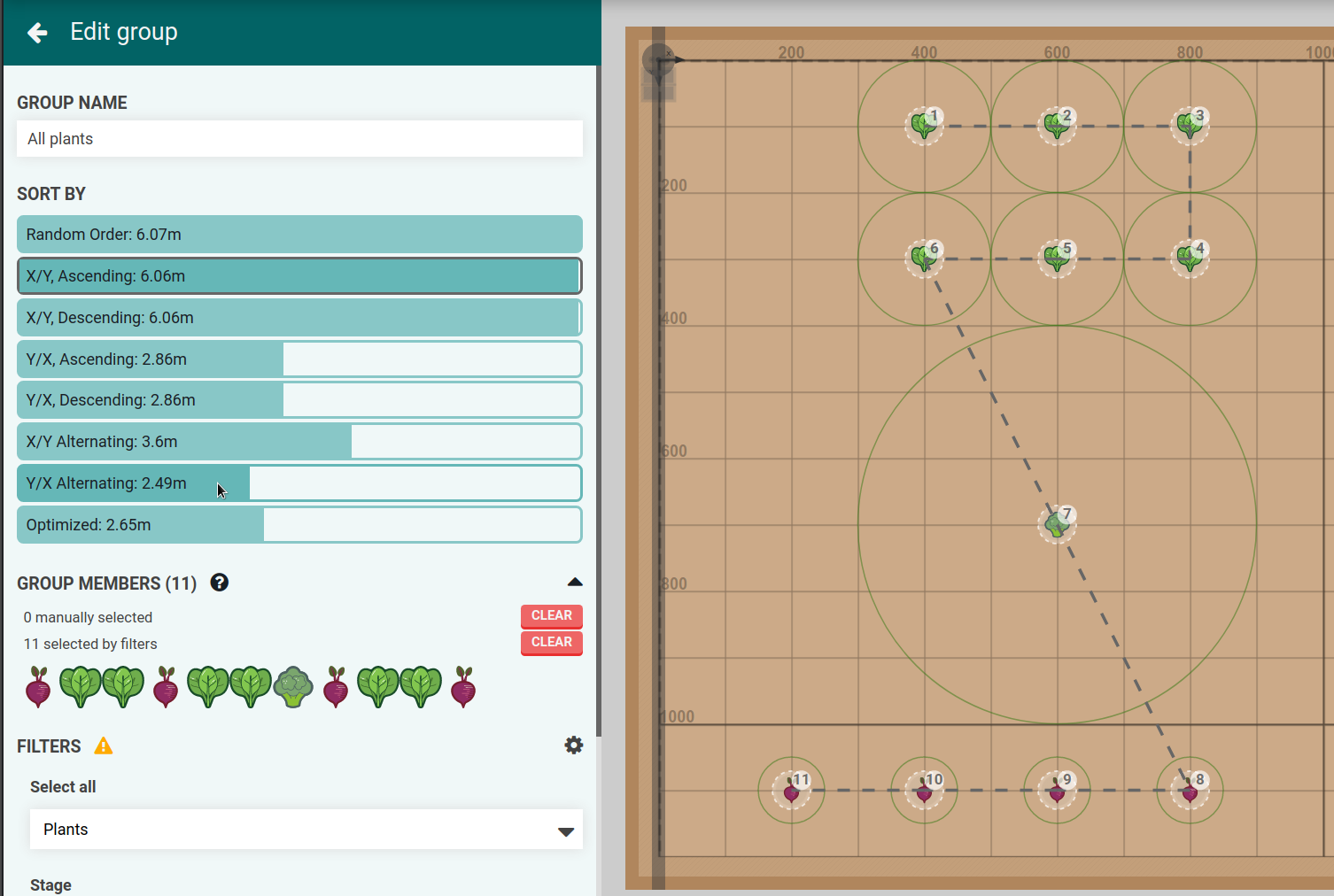
设置
// Example data
var points = [
{ uuid: "1", body: { x: 1, y: 1 } },
{ uuid: "2", body: { x: 2, y: 2 } },
{ uuid: "3", body: { x: 0, y: 10 } },
{ uuid: "4", body: { x: 10, y: 0 } },
{ uuid: "5", body: { x: 10, y: 10 } },
];
// Library
var script = document.createElement('script');
script.type = 'text/javascript';
script.src = 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/lodash@4/lodash.min.js';
document.head.appendChild(script);
随机的
_.shuffle(points)
// sample example data order: 4 1 2 3 5
X/Y 升序
_.sortBy(points, ["body.x", "body.y"])
// expected example data order: 3 1 2 4 5
X/Y 降序
_.sortBy(points, ["body.x", "body.y"]).reverse()
// expected example data order: 5 4 2 1 3
Y/X 升序
_.sortBy(points, ["body.y", "body.x"])
// expected example data order: 4 1 2 3 5
Y/X 降序
_.sortBy(points, ["body.y", "body.x"]).reverse()
// expected example data order: 5 3 2 1 4
X/Y 交替
_.chain(points)
.map(p => p.body.x)
.uniq()
.sortBy()
.map((x, index) =>
index % 2 == 0
? _.sortBy(points.filter(p => p.body.x == x), "body.y")
: _.sortBy(points.filter(p => p.body.x == x), "body.y").reverse())
.flatten()
.value()
// expected example data order: 3 1 2 5 4
Y/X 交替
_.chain(points)
.map(p => p.body.y)
.uniq()
.sortBy()
.map((y, index) =>
index % 2 == 0
? _.sortBy(points.filter(p => p.body.y == y), "body.x")
: _.sortBy(points.filter(p => p.body.y == y), "body.x").reverse())
.flatten()
.value()
// expected example data order: 4 1 2 5 3
优化
最近邻算法:
var ordered = [];
let available = points.filter(p => p);
let from = { x: 0, y: 0 };
points.map(() => {
const nearest = _.sortBy(available.map(p => ({
point: p,
distance: Math.pow(Math.pow(p.body.x - from.x, 2)
+ Math.pow(p.body.y - from.y, 2), 0.5)
})), "distance")[0].point;
ordered.push(nearest);
from = { x: nearest.body.x, y: nearest.body.y };
available = available.filter(p => p.uuid !== nearest.uuid);
});
// expected example data order: 1 2 3 5 4
获取最新文章: 扫一扫右上角的二维码加入“创客智造”公众号



















