PythonRobotics机器人算法库-EKF SLAM
说明:
这是一个基于扩展卡尔曼滤波器的 SLAM 示例
介绍:
"""
Extended Kalman Filter SLAM example
original author: Atsushi Sakai (@Atsushi_twi)
notebook author: Andrew Tu (drewtu2)
"""
import math
import numpy as np
%matplotlib notebook
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# EKF state covariance
Cx = np.diag([0.5, 0.5, np.deg2rad(30.0)])**2 # Change in covariance
# Simulation parameter
Qsim = np.diag([0.2, np.deg2rad(1.0)])**2 # Sensor Noise
Rsim = np.diag([1.0, np.deg2rad(10.0)])**2 # Process Noise
DT = 0.1 # time tick [s]
SIM_TIME = 50.0 # simulation time [s]
MAX_RANGE = 20.0 # maximum observation range
M_DIST_TH = 2.0 # Threshold of Mahalanobis distance for data association.
STATE_SIZE = 3 # State size [x,y,yaw]
LM_SIZE = 2 # LM state size [x,y]
show_animation = True
- 在每个时间步,完成以下操作。- 使用控制函数预测新状态 - 根据估计的状态和测量更新地标位置的信念
def ekf_slam(xEst, PEst, u, z):
"""
Performs an iteration of EKF SLAM from the available information.
:param xEst: the belief in last position
:param PEst: the uncertainty in last position
:param u: the control function applied to the last position
:param z: measurements at this step
:returns: the next estimated position and associated covariance
"""
S = STATE_SIZE
# Predict
xEst, PEst, G, Fx = predict(xEst, PEst, u)
initP = np.eye(2)
# Update
xEst, PEst = update(xEst, PEst, u, z, initP)
return xEst, PEst
def predict(xEst, PEst, u):
"""
Performs the prediction step of EKF SLAM
:param xEst: nx1 state vector
:param PEst: nxn covariance matrix
:param u: 2x1 control vector
:returns: predicted state vector, predicted covariance, jacobian of control vector, transition fx
"""
S = STATE_SIZE
G, Fx = jacob_motion(xEst[0:S], u)
xEst[0:S] = motion_model(xEst[0:S], u)
# Fx is an an identity matrix of size (STATE_SIZE)
# sigma = G*sigma*G.T + Noise
PEst[0:S, 0:S] = G.T @ PEst[0:S, 0:S] @ G + Fx.T @ Cx @ Fx
return xEst, PEst, G, Fx
def motion_model(x, u):
"""
Computes the motion model based on current state and input function.
:param x: 3x1 pose estimation
:param u: 2x1 control input [v; w]
:returns: the resulting state after the control function is applied
"""
F = np.array([[1.0, 0, 0],
[0, 1.0, 0],
[0, 0, 1.0]])
B = np.array([[DT * math.cos(x[2, 0]), 0],
[DT * math.sin(x[2, 0]), 0],
[0.0, DT]])
x = (F @ x) + (B @ u)
return x
def update(xEst, PEst, u, z, initP):
"""
Performs the update step of EKF SLAM
:param xEst: nx1 the predicted pose of the system and the pose of the landmarks
:param PEst: nxn the predicted covariance
:param u: 2x1 the control function
:param z: the measurements read at new position
:param initP: 2x2 an identity matrix acting as the initial covariance
:returns: the updated state and covariance for the system
"""
for iz in range(len(z[:, 0])): # for each observation
minid = search_correspond_LM_ID(xEst, PEst, z[iz, 0:2]) # associate to a known landmark
nLM = calc_n_LM(xEst) # number of landmarks we currently know about
if minid == nLM: # Landmark is a NEW landmark
print("New LM")
# Extend state and covariance matrix
xAug = np.vstack((xEst, calc_LM_Pos(xEst, z[iz, :])))
PAug = np.vstack((np.hstack((PEst, np.zeros((len(xEst), LM_SIZE)))),
np.hstack((np.zeros((LM_SIZE, len(xEst))), initP))))
xEst = xAug
PEst = PAug
lm = get_LM_Pos_from_state(xEst, minid)
y, S, H = calc_innovation(lm, xEst, PEst, z[iz, 0:2], minid)
K = (PEst @ H.T) @ np.linalg.inv(S) # Calculate Kalman Gain
xEst = xEst + (K @ y)
PEst = (np.eye(len(xEst)) - (K @ H)) @ PEst
xEst[2] = pi_2_pi(xEst[2])
return xEst, PEst
def calc_innovation(lm, xEst, PEst, z, LMid):
"""
Calculates the innovation based on expected position and landmark position
:param lm: landmark position
:param xEst: estimated position/state
:param PEst: estimated covariance
:param z: read measurements
:param LMid: landmark id
:returns: returns the innovation y, and the jacobian H, and S, used to calculate the Kalman Gain
"""
delta = lm - xEst[0:2]
q = (delta.T @ delta)[0, 0]
zangle = math.atan2(delta[1, 0], delta[0, 0]) - xEst[2, 0]
zp = np.array([[math.sqrt(q), pi_2_pi(zangle)]])
# zp is the expected measurement based on xEst and the expected landmark position
y = (z - zp).T # y = innovation
y[1] = pi_2_pi(y[1])
H = jacobH(q, delta, xEst, LMid + 1)
S = H @ PEst @ H.T + Cx[0:2, 0:2]
return y, S, H
def jacobH(q, delta, x, i):
"""
Calculates the jacobian of the measurement function
:param q: the range from the system pose to the landmark
:param delta: the difference between a landmark position and the estimated system position
:param x: the state, including the estimated system position
:param i: landmark id + 1
:returns: the jacobian H
"""
sq = math.sqrt(q)
G = np.array([[-sq * delta[0, 0], - sq * delta[1, 0], 0, sq * delta[0, 0], sq * delta[1, 0]],
[delta[1, 0], - delta[0, 0], - q, - delta[1, 0], delta[0, 0]]])
G = G / q
nLM = calc_n_LM(x)
F1 = np.hstack((np.eye(3), np.zeros((3, 2 * nLM))))
F2 = np.hstack((np.zeros((2, 3)), np.zeros((2, 2 * (i - 1))),
np.eye(2), np.zeros((2, 2 * nLM - 2 * i))))
F = np.vstack((F1, F2))
H = G @ F
return H
此处描述的观察步骤在主要 EKF SLAM 过程之外,主要用作驱动模拟的方法。观察功能负责计算机器人的姿势如何随时间变化和累积误差,以及每次测量结果预期的理论测量值
观察基于机器人的真实位置。航位推算误差和控制功能也在这里传递
def observation(xTrue, xd, u, RFID):
"""
:param xTrue: the true pose of the system
:param xd: the current noisy estimate of the system
:param u: the current control input
:param RFID: the true position of the landmarks
:returns: Computes the true position, observations, dead reckoning (noisy) position,
and noisy control function
"""
xTrue = motion_model(xTrue, u)
# add noise to gps x-y
z = np.zeros((0, 3))
for i in range(len(RFID[:, 0])): # Test all beacons, only add the ones we can see (within MAX_RANGE)
dx = RFID[i, 0] - xTrue[0, 0]
dy = RFID[i, 1] - xTrue[1, 0]
d = math.sqrt(dx**2 + dy**2)
angle = pi_2_pi(math.atan2(dy, dx) - xTrue[2, 0])
if d <= MAX_RANGE:
dn = d + np.random.randn() * Qsim[0, 0] # add noise
anglen = angle + np.random.randn() * Qsim[1, 1] # add noise
zi = np.array([dn, anglen, i])
z = np.vstack((z, zi))
# add noise to input
ud = np.array([[
u[0, 0] + np.random.randn() * Rsim[0, 0],
u[1, 0] + np.random.randn() * Rsim[1, 1]]]).T
xd = motion_model(xd, ud)
return xTrue, z, xd, ud
def calc_n_LM(x):
"""
Calculates the number of landmarks currently tracked in the state
:param x: the state
:returns: the number of landmarks n
"""
n = int((len(x) - STATE_SIZE) / LM_SIZE)
return n
def jacob_motion(x, u):
"""
Calculates the jacobian of motion model.
:param x: The state, including the estimated position of the system
:param u: The control function
:returns: G: Jacobian
Fx: STATE_SIZE x (STATE_SIZE + 2 * num_landmarks) matrix where the left side is an identity matrix
"""
# [eye(3) [0 x y; 0 x y; 0 x y]]
Fx = np.hstack((np.eye(STATE_SIZE), np.zeros(
(STATE_SIZE, LM_SIZE * calc_n_LM(x)))))
jF = np.array([[0.0, 0.0, -DT * u[0] * math.sin(x[2, 0])],
[0.0, 0.0, DT * u[0] * math.cos(x[2, 0])],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0]],dtype=object)
G = np.eye(STATE_SIZE) + Fx.T @ jF @ Fx
if calc_n_LM(x) > 0:
print(Fx.shape)
return G, Fx,
def calc_LM_Pos(x, z):
"""
Calculates the pose in the world coordinate frame of a landmark at the given measurement.
:param x: [x; y; theta]
:param z: [range; bearing]
:returns: [x; y] for given measurement
"""
zp = np.zeros((2, 1))
zp[0, 0] = x[0, 0] + z[0] * math.cos(x[2, 0] + z[1])
zp[1, 0] = x[1, 0] + z[0] * math.sin(x[2, 0] + z[1])
#zp[0, 0] = x[0, 0] + z[0, 0] * math.cos(x[2, 0] + z[0, 1])
#zp[1, 0] = x[1, 0] + z[0, 0] * math.sin(x[2, 0] + z[0, 1])
return zp
def get_LM_Pos_from_state(x, ind):
"""
Returns the position of a given landmark
:param x: The state containing all landmark positions
:param ind: landmark id
:returns: The position of the landmark
"""
lm = x[STATE_SIZE + LM_SIZE * ind: STATE_SIZE + LM_SIZE * (ind + 1), :]
return lm
def search_correspond_LM_ID(xAug, PAug, zi):
"""
Landmark association with Mahalanobis distance.
If this landmark is at least M_DIST_TH units away from all known landmarks,
it is a NEW landmark.
:param xAug: The estimated state
:param PAug: The estimated covariance
:param zi: the read measurements of specific landmark
:returns: landmark id
"""
nLM = calc_n_LM(xAug)
mdist = []
for i in range(nLM):
lm = get_LM_Pos_from_state(xAug, i)
y, S, H = calc_innovation(lm, xAug, PAug, zi, i)
mdist.append(y.T @ np.linalg.inv(S) @ y)
mdist.append(M_DIST_TH) # new landmark
minid = mdist.index(min(mdist))
return minid
def calc_input():
v = 1.0 # [m/s]
yawrate = 0.1 # [rad/s]
u = np.array([[v, yawrate]]).T
return u
def pi_2_pi(angle):
return (angle + math.pi) % (2 * math.pi) - math.pi
def main():
print(" start!!")
time = 0.0
# RFID positions [x, y]
RFID = np.array([[10.0, -2.0],
[15.0, 10.0],
[3.0, 15.0],
[-5.0, 20.0]])
# State Vector [x y yaw v]'
xEst = np.zeros((STATE_SIZE, 1))
xTrue = np.zeros((STATE_SIZE, 1))
PEst = np.eye(STATE_SIZE)
xDR = np.zeros((STATE_SIZE, 1)) # Dead reckoning
# history
hxEst = xEst
hxTrue = xTrue
hxDR = xTrue
while SIM_TIME >= time:
time += DT
u = calc_input()
xTrue, z, xDR, ud = observation(xTrue, xDR, u, RFID)
xEst, PEst = ekf_slam(xEst, PEst, ud, z)
x_state = xEst[0:STATE_SIZE]
# store data history
hxEst = np.hstack((hxEst, x_state))
hxDR = np.hstack((hxDR, xDR))
hxTrue = np.hstack((hxTrue, xTrue))
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.cla()
plt.plot(RFID[:, 0], RFID[:, 1], "*k")
plt.plot(xEst[0], xEst[1], ".r")
# plot landmark
for i in range(calc_n_LM(xEst)):
plt.plot(xEst[STATE_SIZE + i * 2],
xEst[STATE_SIZE + i * 2 + 1], "xg")
plt.plot(hxTrue[0, :],
hxTrue[1, :], "-b")
plt.plot(hxDR[0, :],
hxDR[1, :], "-k")
plt.plot(hxEst[0, :],
hxEst[1, :], "-r")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.001)
进入目录PythonRobotics/SLAM/EKFSLAM
执行文件
python3 ekf_slam.py
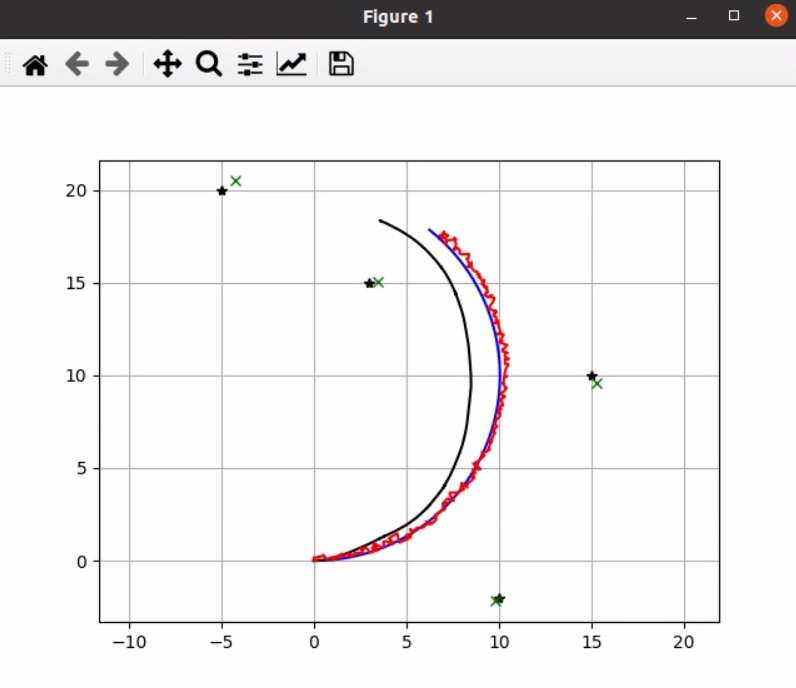
EKF SLAM 的模拟
黑星:地标
绿色十字:地标位置的估计
黑线:航位推算
蓝线:基本事实
红线:EKF SLAM 位置估计结果如下
ekf_slam.py start!!
New LM
New LM
New LM
New LM
获取最新文章: 扫一扫右上角的二维码加入“创客智造”公众号

























