Turtlebot4入门教程-演示-创建节点(Python)
Turtlebot4入门教程-演示-创建节点(Python)
说明:
- 本教程将介绍创建 ROS2 包和用 Python 编写 ROS2 节点的步骤。
- 有关 C++ 示例,请单击此处。
- 这些步骤与 ROS2 教程类似,但侧重于与 TurtleBot 4 的交互。源代码,请单击此处。
- 您可以在 TurtleBot 4 的 Raspberry Pi 或 PC 上学习本教程。
相关设备:
- Turtlebot4机器人套件:采购地址
创建工作区
- 如果您还没有工作区,请打开一个终端并在您选择的目录中创建一个:
mkdir ~/turtlebot4_ws/src -p
创建包和节点
- 您将需要创建一个 ROS2 包来保存您的文件。
- 在本教程中,我们将创建一个名为 turtlebot4_python_tutorials 的包,其中包含一个名为 turtlebot4_first_python_node 的节点。
source /opt/ros/galactic/setup.bash
cd ~/turtlebot4_ws/src
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_python --node-name turtlebot4_first_python_node turtlebot4_python_tutorials
- 这将创建一个 turtlebot4_python_tutorials 文件夹并使用基本的“Hello World”节点以及 ROS2 Python 包所需的 setup 和 package.xml 文件填充它。
写你的节点
- 下一步是开始编码。
- 对于本教程,我们的目标是使用 Create® 3 界面按钮 1 更改 Create® 3 灯环的颜色。
- 在您最喜欢的文本编辑器中打开位于 ~/turtlebot4_ws/src/turtlebot4_python_tutorials/turtlebot4_python_tutorials/turtlebot4_first_python_node.py 的“Hello World”.py 文件。
添加您的依赖项
- 对于本教程,我们将需要使用 rclpy 和 irobot_create_msgs 包。
- rclpy 包允许我们创建 ROS2 节点,并让我们可以完全访问 Python 中的所有基本 ROS2 功能。
- irobot_create_msgs 包使我们能够访问 Create® 3 用于读取按钮按下和控制灯环的自定义消息。
- 在 package.xml 中,在 <buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend> 下添加这些行:
<depend>rclpy</depend>
<depend>irobot_create_msgs</depend>
- 在您的 .py 文件中,导入这些包:
from irobot_create_msgs.msg import InterfaceButtons, LightringLeds
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import qos_profile_sensor_data
创建一个类
- 现在已经设置了依赖项,我们可以创建一个继承自 rclpy.Node 类的类。 我们将这个类称为 TurtleBot4FirstNode。
class TurtleBot4FirstNode(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('turtlebot4_first_python_node')
请注意,我们的类调用 super() 构造函数并将我们的节点名称turtlebot4_first_python_node 传递给它。
我们现在可以在主函数中创建我们的节点并旋转它。 由于我们的节点是空的,节点将被创建但它不会做任何事情。
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
node = TurtleBot4FirstNode()
rclpy.spin(node)
node.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
订阅 Create® 3 界面按钮
- 我们的下一步是订阅 Create® 3 界面按钮主题以接收按钮按下。
- 我们需要为订阅创建一个 rclpy.Subscription 以及一个回调函数。
- 每次我们收到关于界面按钮主题的消息时,都会调用回调函数。
class TurtleBot4FirstNode(Node):
lights_on_ = False
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('turtlebot4_first_python_node')
# Subscribe to the /interface_buttons topic
self.interface_buttons_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
InterfaceButtons,
'/interface_buttons',
self.interface_buttons_callback,
qos_profile_sensor_data)
# Interface buttons subscription callback
def interface_buttons_callback(self, create3_buttons_msg: InterfaceButtons):
注意 interface_buttons_subscriber 使用 InterfaceButtons 消息类型,服务质量是 qos_profile_sensor_data。 这些参数必须与主题匹配,否则订阅会失败。
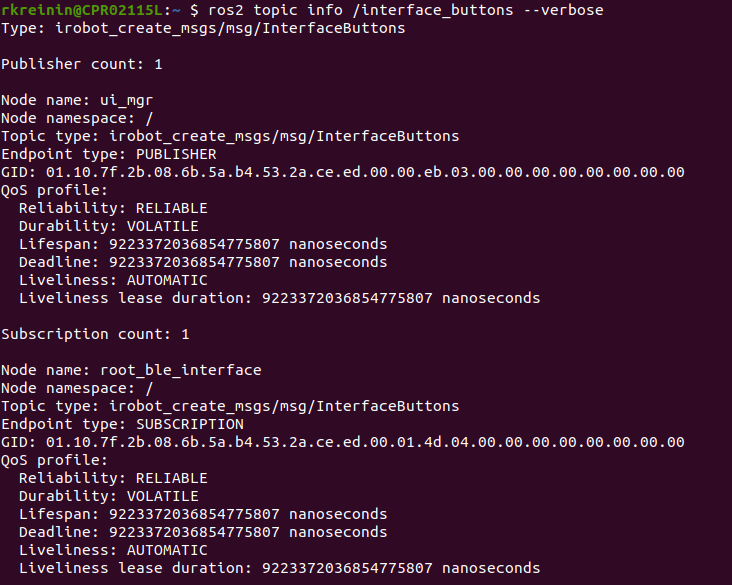
如果您不确定主题使用的是什么消息类型或 QoS,您可以使用 ROS2 CLI 查找此信息。
调用 ros2 topic info /
--verbose 以获取完整的详细信息。
Test Create® 3 Button 1
- 现在我们已经订阅了,让我们通过在每次按下按钮 1 时打印一条消息来测试我们的节点。
- 编辑界面按钮回调函数,如下所示:
# Interface buttons subscription callback
def interface_buttons_callback(self, create3_buttons_msg: InterfaceButtons):
# Button 1 is pressed
if create3_buttons_msg.button_1.is_pressed:
self.get_logger().info('Button 1 Pressed!')
现在,每次我们收到关于 /interface_buttons 主题的消息时,我们都会检查按钮 1 是否被按下,如果是,则节点将打印一条消息。
为了测试这一点,我们需要使用 colcon 构建我们的包:
cd ~/turtlebot4_ws
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select turtlebot4_python_tutorials
source install/local_setup.bash
--symlink-install允许我们安装指向 Python 脚本的符号链接,而不是脚本的副本。 这意味着我们对脚本所做的任何更改都将应用于已安装的脚本,因此我们不需要在每次更改后重新构建包。--packages-select标志允许您输入要构建的任意数量的包,以防您不想在工作区中构建所有包。现在,尝试运行节点:
ros2 run turtlebot4_python_tutorials turtlebot4_first_python_node
当你运行它时,在你按下 TurtleBot 4 上的按钮 1 之前什么都不会发生。
按下按钮,您应该会在终端中看到以下消息:
[INFO] [1652384338.145094927] [turtlebot4_first_python_node]: Button 1 Pressed!
- 像这样打印消息是调试代码的好方法。
创建灯光发布者
- 现在我们可以接收到按钮按下,让我们创建一个 lightring 发布者。
class TurtleBot4FirstNode(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('turtlebot4_first_python_node')
# Subscribe to the /interface_buttons topic
self.interface_buttons_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
InterfaceButtons,
'/interface_buttons',
self.interface_buttons_callback,
qos_profile_sensor_data)
# Create a publisher for the /cmd_lightring topic
self.lightring_publisher = self.create_publisher(
LightringLeds,
'/cmd_lightring',
qos_profile_sensor_data)
- Lightring 发布者使用 LightringLeds 消息类型。
- 接下来,让我们创建一个将填充 LightringLeds 消息并发布它的函数。
- 在您的 interface_buttons_callback 函数下方添加此代码:
def button_1_function(self):
# Create a ROS2 message
lightring_msg = LightringLeds()
# Stamp the message with the current time
lightring_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
# Override system lights
lightring_msg.override_system = True
# LED 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[0].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].green = 0
# LED 1
lightring_msg.leds[1].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[1].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[1].green = 0
# LED 2
lightring_msg.leds[2].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].green = 255
# LED 3
lightring_msg.leds[3].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].green = 0
# LED 4
lightring_msg.leds[4].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[4].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[4].green = 255
# LED 5
lightring_msg.leds[5].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[5].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[5].green = 255
# Publish the message
self.lightring_publisher.publish(lightring_msg)
- 此函数创建一个 LightringLeds 消息并填充参数。
- 我们首先用当前时间标记消息:
lightring_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
- 然后我们将 override_system 参数设置为 True,以便我们的命令覆盖 Create® 3 发送到 lightring 的任何命令。
lightring_msg.override_system = True
- 接下来,我们用我们想要的任何颜色填充 LED 阵列中的 6 个 LED。
# LED 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[0].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].green = 0
# LED 1
lightring_msg.leds[1].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[1].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[1].green = 0
# LED 2
lightring_msg.leds[2].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].green = 255
# LED 3
lightring_msg.leds[3].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].green = 0
# LED 4
lightring_msg.leds[4].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[4].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[4].green = 255
# LED 5
lightring_msg.leds[5].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[5].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[5].green = 255
- 每个 RGB 值可以设置在 0 到 255 之间。您可以查找任何颜色的 RGB 值并在此处进行设置。
- 最后,我们发布消息。
self.lightring_publisher.publish(lightring_msg)
- 按下按钮发布 lightring 命令
- 现在我们可以将我们的界面按钮订阅连接到我们的 lightring 发布者。
- 只需在 interface_buttons_callback 中调用 button_1_function。
# Interface buttons subscription callback
def interface_buttons_callback(self, create3_buttons_msg: InterfaceButtons):
# Button 1 is pressed
if create3_buttons_msg.button_1.is_pressed:
self.get_logger().info('Button 1 Pressed!')
self.button_1_function()
- 通过像以前一样运行节点来测试它。
- 按下按钮 1,lightring 灯应如下所示:
lightring
切换灯环
您会注意到,一旦您设置了 lightrings LED,它们将永远保持这种状态。 让按钮在每次按下时打开或关闭灯。
添加一个布尔值来跟踪灯光状态:
class TurtleBot4FirstNode(Node):
lights_on_ = False
def __init__(self):
- 并修改 button_1_function 来切换灯光:
# Perform a function when Button 1 is pressed
def button_1_function(self):
# Create a ROS2 message
lightring_msg = LightringLeds()
# Stamp the message with the current time
lightring_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
# Lights are currently off
if not self.lights_on_:
# Override system lights
lightring_msg.override_system = True
# LED 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[0].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].green = 0
# LED 1
lightring_msg.leds[1].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[1].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[1].green = 0
# LED 2
lightring_msg.leds[2].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].green = 255
# LED 3
lightring_msg.leds[3].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].green = 0
# LED 4
lightring_msg.leds[4].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[4].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[4].green = 255
# LED 5
lightring_msg.leds[5].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[5].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[5].green = 255
# Lights are currently on
else:
# Disable system override. The system will take back control of the lightring.
lightring_msg.override_system = False
# Publish the message
self.lightring_publisher.publish(lightring_msg)
# Toggle the lights on status
self.lights_on_ = not self.lights_on_
- 现在,如果我们再次按下按钮 1,Create® 3 将重新获得对光环的控制。
你的第一个 Python 节点
- 你已经完成了你的第一个 Python 节点的编写! 最终的 .py 文件应如下所示:
from irobot_create_msgs.msg import InterfaceButtons, LightringLeds
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import qos_profile_sensor_data
class TurtleBot4FirstNode(Node):
lights_on_ = False
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('turtlebot4_first_python_node')
# Subscribe to the /interface_buttons topic
self.interface_buttons_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
InterfaceButtons,
'/interface_buttons',
self.interface_buttons_callback,
qos_profile_sensor_data)
# Create a publisher for the /cmd_lightring topic
self.lightring_publisher = self.create_publisher(
LightringLeds,
'/cmd_lightring',
qos_profile_sensor_data)
# Interface buttons subscription callback
def interface_buttons_callback(self, create3_buttons_msg: InterfaceButtons):
# Button 1 is pressed
if create3_buttons_msg.button_1.is_pressed:
self.get_logger().info('Button 1 Pressed!')
self.button_1_function()
# Perform a function when Button 1 is pressed
def button_1_function(self):
# Create a ROS2 message
lightring_msg = LightringLeds()
# Stamp the message with the current time
lightring_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
# Lights are currently off
if not self.lights_on_:
# Override system lights
lightring_msg.override_system = True
# LED 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[0].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[0].green = 0
# LED 1
lightring_msg.leds[1].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[1].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[1].green = 0
# LED 2
lightring_msg.leds[2].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[2].green = 255
# LED 3
lightring_msg.leds[3].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[3].green = 0
# LED 4
lightring_msg.leds[4].red = 255
lightring_msg.leds[4].blue = 0
lightring_msg.leds[4].green = 255
# LED 5
lightring_msg.leds[5].red = 0
lightring_msg.leds[5].blue = 255
lightring_msg.leds[5].green = 255
# Lights are currently on
else:
# Disable system override. The system will take back control of the lightring.
lightring_msg.override_system = False
# Publish the message
self.lightring_publisher.publish(lightring_msg)
# Toggle the lights on status
self.lights_on_ = not self.lights_on_
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
node = TurtleBot4FirstNode()
rclpy.spin(node)
node.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
获取最新文章: 扫一扫右上角的二维码加入“创客智造”公众号



















