Galactic Geochelone (galactic)
Galactic Geochelone 是 ROS 2 的第七个版本。 以下是自上一个版本以来 Galactic Geochelone 中重要变化和功能的重点介绍。 有关自 Foxy 以来所有变化的列表,请参阅“长格式变更日志 <Galactic-Geochelone-Complete-Changelog>”。
支持的平台
Galactic Geochelone 主要支持以下平台:
一级平台:
Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal):
amd64andarm64Windows 10 (Visual Studio 2019):
amd64
二级平台:
RHEL 8:
amd64
三级平台:
Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal):
arm32Debian Bullseye (11):
amd64,arm64andarm32OpenEmbedded Thud (2.6) / webOS OSE:
arm32andarm64Mac macOS 10.14 (Mojave):
amd64
有关 RMW 实现、编译器/解释器版本和系统依赖版本的更多信息,请参阅 REP 2000。
安装
此 ROS 2 版本中的新功能
能够指定每个记录器的日志级别
现在可以在命令行上为不同的记录器指定不同的日志级别:
ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker --ros-args --log-level WARN --log-level talker:=DEBUG
上述命令设置了全局日志级别为 WARN,但将 talker 节点消息的日志级别设置为 DEBUG。
命令行选项 --log-level 可以传递任意次数,为每个记录器设置不同的日志级别。
能够通过环境变量配置日志目录
现在可以通过两个环境变量配置日志目录:ROS_LOG_DIR 和 ROS_HOME。
逻辑如下:
如果设置了“ROS_LOG_DIR”且不为空,则使用“$ROS_LOG_DIR”。
否则,使用“$ROS_HOME/log”,如果未设置或为空,则使用“~/.ros”作为“ROS_HOME”。
因此默认值保持不变:“~/.ros/log”。
相关 PR:ros2/rcl_logging#53 和 ros2/launch#460。
例如:
ROS_LOG_DIR=/tmp/foo ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker
将会把所有日志放在“/tmp/foo”中。
ROS_HOME=/path/to/home ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker
将所有日志放在 /path/to/home/log 中。
能够在 CMake 之外调用 rosidl 管道
现在可以直接在 CMake 之外调用 rosidl 接口生成管道。
源代码生成器和接口定义转换器可通过统一的命令行界面访问。
例如,在某些 demo 包中给出一个 Demo 消息,例如:
mkdir -p demo/msg
cd demo
cat << EOF > msg/Demo.msg
std_msgs/Header header
geometry_msgs/Twist twist
geometry_msgs/Accel accel
EOF
可以轻松生成 C、C++ 和 Python 支持源代码:
rosidl generate -o gen -t c -t cpp -t py -I$(ros2 pkg prefix --share std_msgs)/.. \
-I$(ros2 pkg prefix --share geometry_msgs)/.. demo msg/Demo.msg
生成的源代码将放在 gen 目录中。
还可以将消息定义转换为不同的格式,以供第三方代码生成工具使用:
rosidl translate -o gen --to idl -I$(ros2 pkg prefix --share std_msgs)/.. \
-I$(ros2 pkg prefix --share geometry_msgs)/.. demo msg/Demo.msg
翻译后的消息定义将放在 gen 目录中。
请注意,这些工具会生成源代码,但不会构建源代码——该责任仍在调用者身上。
这是在 CMake 以外的构建系统中启用 rosidl 接口生成的第一步。
有关进一步参考和后续步骤,请参阅 设计文档。
在启动时从外部配置 QoS
现在可以在启动时从外部配置节点的 QoS 设置。 QoS 设置在运行时**不可**配置;它们只能在启动时配置。 节点作者必须选择启用在启动时更改 QoS 设置。 如果在节点上启用了该功能,则可以在节点首次启动时使用 ROS 参数设置 QoS 设置。
Demos in C++ and Python can be found here.
有关更多详细信息,请参阅“设计文档<http://design.ros2.org/articles/qos_configurability.html>”。
请注意,使用已注册回调处理参数更改的用户代码应避免拒绝未知参数的更新。 在 Galactic 之前,这被认为是不好的做法,但在启用外部可配置 QoS 的情况下,它将导致硬故障。
相关 PR:ros2/rclcpp#1408 和 ros2/rclpy#635
可用的 Python point_cloud2 实用程序
用于与 Python 中的 PointCloud2 消息 交互的几个实用程序已 移植到 ROS 2。 这些实用程序允许从 PointCloud2 消息(“read_points” 和 “read_points_list”)获取点列表,并从点列表(“create_cloud” 和 “create_cloud_xyz32”)创建 PointCloud2 消息。
创建 PointCloud 2 消息然后读回的示例:
import sensor_msgs_py.point_cloud2
from std_msgs.msg import Header
pointlist = [[0.0, 0.1, 0.2]]
pointcloud = sensor_msgs_py.point_cloud2.create_cloud_xyz32(Header(frame_id='frame'), pointlist)
for point in sensor_msgs_py.point_cloud2.read_points(pointcloud):
print(point)
RViz2 时间面板
Rviz2 时间面板显示当前 Wall 和 ROS 时间以及经过的 Wall 和 ROS 时间,已“移植到 RViz2 <https://github.com/ros2/rviz/pull/599>”__。
要启用时间面板,请单击面板 -> 添加新面板,然后选择“时间”。
将出现如下所示的面板:

ros2 topic echo 可以打印序列化数据
调试中间件问题时,查看 RMW 发送的原始序列化数据会很有用。
–raw 命令行标志 已添加到 ros2 topic echo 以显示此数据。
要查看实际效果,请运行以下命令。
终端1
$ ros2 topic pub /chatter std_msgs/msg/String "data: 'hello'"
终端2
$ ros2 topic echo --raw /chatter
b'\x00\x01\x00\x00\x06\x00\x00\x00hello\x00\x00\x00'
---
获取消息的 YAML 表示
现在可以使用 to_yaml 函数获取 C++ 中所有消息的 YAML 表示。 打印出 YAML 表示的代码示例:
#include <cstdio>
#include <std_msgs/msg/string.hpp>
int main()
{
std_msgs::msg::String msg;
msg.data = "hello world";
printf("%s", rosidl_generator_traits::to_yaml(msg).c_str());
return 0;
}
能够通过 ros2 命令在运行时加载参数文件
ROS 2 长期以来一直能够在启动时指定参数值(通过命令行参数或 YAML 文件),并将当前参数转储到文件(通过“ros2 param dump”)。 Galactic 增加了使用“ros2 param load”动词从 YAML 文件“在运行时加载参数值<https://github.com/ros2/ros2cli/pull/590>”的能力。 例如:
终端1:
$ ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp parameter_blackboard
终端2:
$ ros2 param set /parameter_blackboard foo bar # sets 'foo' parameter to value 'bar'
$ ros2 param dump /parameter_blackboard # dumps current value of parameters to ./parameter_blackboard.yaml
$ ros2 param set /parameter_blackboard foo different # sets 'foo' parameter to value 'different'
$ ros2 param load /parameter_blackboard ./parameter_blackboard.yaml # reloads previous state of parameters, 'foo' is back to 'bar'
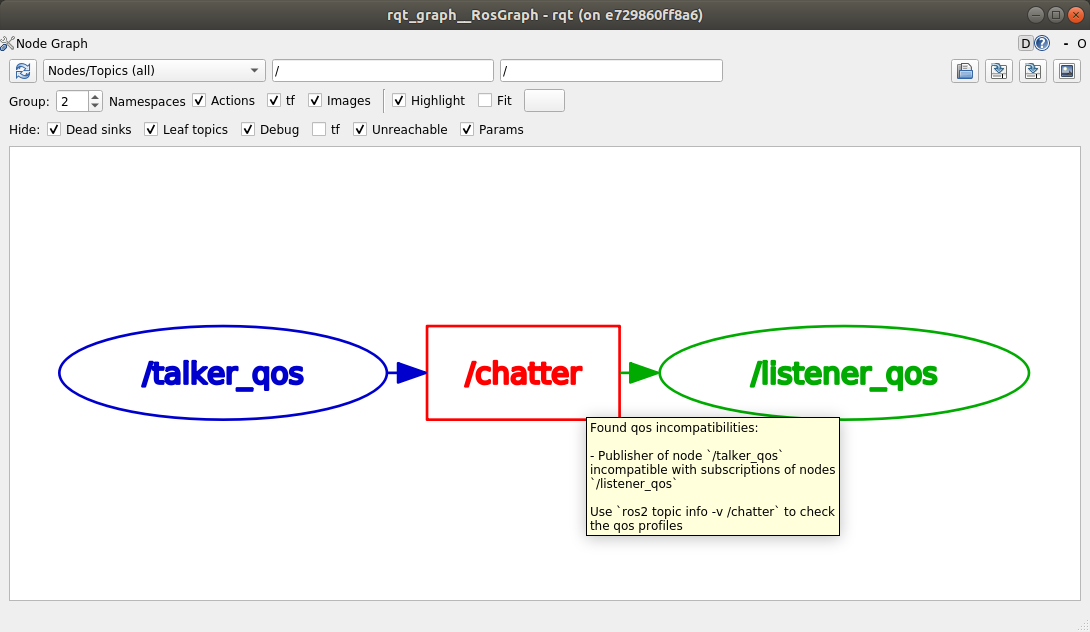
Tools to check for QoS incompatibilities
基于新的 QoS 兼容性检查 API,ros2doctor 和 rqt_graph 现在可以检测并报告发布者和订阅者之间的 QoS 不兼容性。
假设发布者和订阅者的 QoS 设置不兼容 <../../Concepts/Intermediate/About-Quality-of-Service-Settings>:
终端 1:
$ ros2 run demo_nodes_py talker_qos -n 1000 # i.e. best_effort publisher
终端 2:
$ ros2 run demo_nodes_py listener_qos --reliable -n 1000 # i.e. reliable subscription
ros2doctor reports:
$ ros2 doctor --report
# ...
QOS COMPATIBILITY LIST
topic [type] : /chatter [std_msgs/msg/String]
publisher node : talker_qos
subscriber node : listener_qos
compatibility status : ERROR: Best effort publisher and reliable subscription;
# ...
while rqt_graph shows:
在参数文件中使用启动替换
就像 ROS 1 roslaunch 中的 rosparam 标签一样,launch_ros 现在可以评估参数文件中的替换。
例如,给定一些 parameter_file_with_substitutions.yaml,如下所示:
/**:
ros__parameters:
launch_date: $(command date)
将 allow_substs 设置为 True 以在 Node 启动时评估替换:
import launch
import launch_ros.parameter_descriptions
import launch_ros.actions
def generate_launch_description():
return launch.LaunchDescription([
launch_ros.actions.Node(
package='demo_nodes_cpp',
executable='parameter_blackboard',
parameters=[
launch_ros.parameter_descriptions.ParameterFile(
param_file='parameter_file_with_substitutions.yaml',
allow_substs=True)
]
)
])
XML 启动文件也支持此功能。
<launch>
<node pkg="demo_nodes_cpp" exec="parameter_blackboard">
<param from="parameter_file_with_substitutions.yaml" allow_substs="true"/>
</node>
</launch>
相关 PR:ros2/launch_ros#168
支持独特的网络流
应用程序现在可能需要 UDP/TCP 和基于 IP 的 RMW 实现来为发布者和订阅者提供独特的*网络流*(即独特的`差异化服务代码点<https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2474>`_ 和/或独特的`IPv6 流标签<https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6437>`_ 和/或 IP 数据包头中的独特端口),从而在支持此类功能的网络架构(如 5G 网络)中为这些 IP 流启用 QoS 规范。
要查看实际效果,您可以运行这些 C++ 示例(可在 ros2/examples 存储库中找到):
终端 1:
ros2 run examples_rclcpp_minimal_publisher publisher_member_function_with_unique_network_flow_endpoints
终端 2:
ros2 run examples_rclcpp_minimal_subscriber subscriber_member_function_with_unique_network_flow_endpoints
参考 Unique Network Flows design document 以供进一步参考。
Rosbag2 新功能
按时间分割记录
在 Foxy 中,您只能按包的大小分割正在录制的包,现在您还可以按经过的时间分割。 以下命令将包文件分割成 100 秒的块。
ros2 bag record --all --max-bag-duration 100
ros2 bag list
这个新命令列出了 rosbag2 使用的各种类型的已安装插件。
$ ros2 bag list storage
rosbag2_v2
sqlite3
$ ros2 bag list converter
rosbag_v2_converter
压缩实现是一个插件
在 Foxy 中,rosbag2 压缩是使用 Zstd 库实现进行硬编码的。
这已重新设计,因此压缩实现是一个插件,并且可以在不修改核心 rosbag2 代码库的情况下进行交换。
“ros-galactic-rosbag2”附带的默认插件仍然是 Zstd 插件 - 但现在可以发布和使用更多插件,并且可以通过有选择地安装软件包将 Zstd 排除在安装之外。
按消息压缩
在 Foxy 中,您可以在拆分每个 rosbag 文件时自动对其进行压缩(按文件压缩),但现在您还可以指定按消息压缩。
ros2 bag record --all --compression-format zstd --compression-mode message
Rosbag2 Python API
Galactic 中发布了一个新包 rosbag2_py,它提供了一个 Python API。
这个包是围绕 C++ API 的 pybind11 绑定。
截至最初的 Galactic 版本,它尚未公开通过 rosbag2_cpp API 提供的所有功能,但它是 ros2 bag CLI 工具的唯一连接,因此有很多功能可用。
性能测试包和性能改进
自 Foxy 发布以来,对 rosbag2 进行了彻底的性能分析项目。 完整的初始报告可在以下位置获得https://github.com/ros2/rosbag2/blob/galactic/rosbag2_performance/rosbag2_performance_benchmarking/docs/rosbag2_performance_improvements.pdf 。 软件包“rosbag2_performance_benchmarking”提供了运行性能分析(尤其是记录分析)的工具,这有助于我们维护和提高 rosbag2 的性能。
根据这份报告,我们完成了关键工作,将性能提高到更适合实际机器人工作流程的状态。 重点介绍一个关键指标 - 在高带宽压力测试(200Mbps)中,Foxy 版本丢失了高达 70% 的消息,而 Galactic 版本的消息保留率约为 100%。 有关更多详细信息,请参阅链接的报告。
--regex 和 --exclude 选项用于主题选择
新的记录选项 --regex 和 --exclude 允许对包中记录的主题进行微调,而无需明确列出所有主题。
这些选项可以一起使用或单独使用,也可以与 --all 结合使用
以下命令将仅记录名称中带有“scan”的主题。
ros2 bag record --regex "*scan*"
以下命令将记录除“/my_namespace/”中的主题之外的所有主题
ros2 bag record --all --exclude "/my_namespace/*"
ros2 bag reindex
ROS 2 包由目录而不是单个文件表示。
此目录包含一个 metadata.yaml 文件和一个或多个包文件。
当 metadata.yaml 文件丢失或缺失时,ros2 bag reindex $bag_dir 将尝试通过读取目录中的所有包文件来重建它。
播放时间控制
为 rosbag2 播放添加了新控件 - 暂停和恢复、更改速率和播放下一个。 从 Galactic 版本开始,这些控件仅作为 rosbag2 播放器节点上的服务公开。 正在开发将它们公开给键盘控件以及``ros2 bag play`` 中的键盘控件,但在此之前,可以轻松实现带有按钮或键盘控件的用户应用程序来调用这些服务。
# In one shell
$ ros2 bag play my_bag
# In another shell
$ ros2 service list -t
/rosbag2_player/get_rate [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/GetRate]
/rosbag2_player/is_paused [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/IsPaused]
/rosbag2_player/pause [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/Pause]
/rosbag2_player/play_next [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/PlayNext]
/rosbag2_player/resume [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/Resume]
/rosbag2_player/set_rate [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/SetRate]
/rosbag2_player/toggle_paused [rosbag2_interfaces/srv/TogglePaused]
# Check if playback is paused
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/is_paused rosbag2_interfaces/IsPaused
# Pause playback
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/pause rosbag2_interfaces/Pause
# Resume playback
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/resume rosbag2_interfaces/Resume
# Change the paused state of playback to its opposite. If playing, pauses. If paused, resumes.
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/toggle_paused rosbag2_interfaces/TogglePaused
# Get the current playback rate
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/get_rate
# Set the current playback rate (must be > 0)
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/set_rate rosbag2_interfaces/SetRate "rate: 0.1"
# Play a single next message (only works while paused)
$ ros2 service call /rosbag2_player/play_next rosbag2_interfaces/PlayNext
播放发布 /clock
Rosbag2 还可以通过在播放期间发布到 /clock 主题来指示“模拟时间”。
以下命令将定期发布时钟消息。
# Publish at default rate - 40Hz
ros2 bag play my_bag --clock
# Publish at specific rate - 100Hz
ros2 bag play my_bag --clock 100
自 Foxy 发布以来的变化
默认 RMW 更改为 Eclipse Cyclone DDS
在 Galactic 开发过程中,ROS 2 技术指导委员会`投票<https://discourse.ros.org/t/ros-2-galactic-default-middleware-announced/18064>`__ 将默认 ROS 中间件 (RMW) 更改为`Eclipse Foundation <https://www.eclipse.org>`__ 的`Eclipse Cyclone DDS <https://github.com/eclipse-cyclonedds/cyclonedds>`__ 项目。
无需任何配置更改,用户将默认获得 Eclipse Cyclone DDS。
Fast DDS 和 Connext 仍然是 Tier-1 支持的 RMW 供应商,用户可以通过使用 RMW_IMPLEMENTATION 环境变量自行选择使用其中一个 RMW。
有关更多信息,请参阅`使用多个 RMW 实现指南 <../../How-To-Guides/Working-with-multiple-RMW-implementations>`。
Connext RMW 更改为 rmw_connextdds
一个名为 rmw_connextdds 的 Connext 新 RMW 已合并到 Galactic。
此 RMW 具有更好的性能,并修复了旧 RMW rmw_connext_cpp 的许多问题。
测试和整体质量大幅提升
Galactic 包含许多更改,可修复竞争条件、堵塞内存泄漏和修复用户报告的问题。
除了这些更改之外,在 Galactic 开发过程中,我们还通过实施 REP 2004 来提高系统的整体质量。
rclcpp 包及其所有依赖项(包括大多数 ROS 2 非 Python 核心包)通过以下方式提升至 质量等级 1:
制定版本策略(QL1 要求 1)
制定记录的变更控制流程(QL1 要求 2)
记录所有功能和公共 API(QL1 要求 3)
添加许多额外测试(QL1 要求 4):
对所有功能进行系统测试
对所有公共 API 进行单元测试
每晚性能测试
代码覆盖率为 95%
使包的所有运行时依赖项至少与包一样高(QL1 要求 5)
支持所有 REP-2000 平台(QL1 要求 6)
制定漏洞披露策略(QL1 要求 7)
rmw
用于检查 QoS 配置文件兼容性的新 API
rmw_qos_profile_check_compatible 是一个用于检查两个 QoS 配置文件兼容性的新功能。
RMW 供应商应该在“rqt_graph”等工具中实现此 API,以便 QoS 调试和自省功能能够正常工作。
相关 PR: ros2/rmw#299
ament_cmake
ament_install_python_package() 现在安装一个 Python egg
通过安装平面 Python egg,可以使用“pkg_resources”和“importlib.metadata”等模块发现使用“ament_install_python_package()”安装的 Python 包。此外,还可以在“setup.cfg”文件中提供其他元数据(包括入口点)。
相关 PR:ament/ament_cmake#326
ament_target_dependencies() 处理 SYSTEM 依赖项
现在可以将某些软件包依赖项标记为 SYSTEM 依赖项,以帮助处理外部代码中的警告。通常,SYSTEM 依赖项也会从依赖项计算中排除 - 请谨慎使用它们。
相关 PR:ament/ament_cmake#297
tf2_ros Python 从 tf2_ros 中分离出来
以前存在于 tf2_ros 中的 Python 代码已移至名为 tf2_ros_py 的自己的包中。 任何依赖于 tf2_ros 的现有 Python 代码将继续工作,但这些包的 package.xml 应修改为 tf2_ros_py 上的“exec_depend”。
tf2_ros Python TransformListener 使用全局命名空间
Python TransformListener 现在订阅全局命名空间中的 /tf 和 /tf_static。
以前,它是在节点的命名空间中进行订阅。
这意味着节点的命名空间将不再对 /tf 和 /tf_static 订阅产生影响。
例如:
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo --ros-args -r __ns:=/test -- odom base_link
将订阅“/tf”和“/tf_static”,如“ros2主题列表”所示。
相关 PR: ros2/geometry2#390
rclcpp
spin_until_future_complete 模板参数的变化
Executor::spin_until_future_complete 的第一个模板参数是未来结果类型 ResultT,并且该方法仅接受 std::shared_future<ResultT>。
为了接受其他类型的未来(例如:std::future),该参数已更改为未来类型本身。
在 spin_until_future_complete 调用依赖于模板参数推导的地方,无需进行任何更改。
如果不是,这是一个示例差异:
std::shared_future<MyResultT> future;
...
-executor.spin_until_future_complete<MyResultT>(future);
+executor.spin_until_future_complete<std::shared_future<MyResultT>>(future);
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 ros2/rclcpp#1160。 有关用户代码中所需更改的示例,请参阅 ros-visualization/interactive_markers#72。
默认 /clock 订阅 QoS 配置文件中的更改
默认从历史深度为 10 的可靠通信更改为历史深度为 1 的尽力而为通信。
请参阅 ros2/rclcpp#1312。
可等待 API
修改了可等待 API,以避免与 MultiThreadedExecutor 相关的问题。
这仅影响实现自定义可等待的用户。 有关更多详细信息,请参阅 ros2/rclcpp#1241。
rclcpp 日志记录中的更改宏
以前,日志记录宏容易受到`格式字符串攻击<https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/Format_string_attack>`_,其中格式字符串被评估并且可能执行代码,读取堆栈或在正在运行的程序中导致分段错误。 为了解决这个安全问题,日志记录宏现在只接受字符串文字作为其格式字符串参数。
如果您以前有这样的代码:
const char *my_const_char_string format = "Foo";
RCLCPP_DEBUG(get_logger(), my_const_char_string);
你现在应该用以下方式替换它:
const char *my_const_char_string format = "Foo";
RCLCPP_DEBUG(get_logger(), "%s", my_const_char_string);
或者:
RCLCPP_DEBUG(get_logger(), "Foo");
此更改消除了日志记录宏的一些便利性,因为 std::strings 不再被接受为格式参数。
如果您之前的代码没有格式参数,例如:
std::string my_std_string = "Foo";
RCLCPP_DEBUG(get_logger(), my_std_string);
你现在应该用以下方式替换它:
std::string my_std_string = "Foo";
RCLCPP_DEBUG(get_logger(), "%s", my_std_string.c_str());
如果您使用 std::string 作为带有格式参数的格式字符串,则将该字符串转换为 char * 并将其用作格式字符串将产生格式安全警告。这是因为编译器无法在编译时自省 std::string 来验证参数。为了避免安全警告,我们建议您手动构建字符串并将其传入,而不使用任何格式参数,就像上一个示例一样。
std::stringstream 类型仍可作为流日志记录宏的参数接受。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 ros2/rclcpp#1442。
参数类型现在默认为静态
以前,设置参数时可以更改参数的类型。 例如,如果将参数声明为整数,则稍后调用设置参数可能会将该类型更改为字符串。 这种行为可能会导致错误,并且很少是用户想要的。 从 Galactic 开始,参数类型默认为静态,尝试更改类型将失败。 如果需要以前的动态行为,则有一种机制可以选择它(参见下面的代码)。
// declare integer parameter with default value, trying to set it to a different type will fail.
node->declare_parameter("my_int", 5);
// declare string parameter with no default and mandatory user provided override.
// i.e. the user must pass a parameter file setting it or a command line rule -p <param_name>:=<value>
node->declare_parameter("string_mandatory_override", rclcpp::PARAMETER_STRING);
// Conditionally declare a floating point parameter with a mandatory override.
// Useful when the parameter is only needed depending on other conditions and no default is reasonable.
if (mode == "modeA") {
node->declare_parameter("conditionally_declare_double_parameter", rclcpp::PARAMETER_DOUBLE);
}
// You can also get the old dynamic typing behavior if you want:
rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterDescriptor descriptor;
descriptor.dynamic_typing = true;
node->declare_parameter("dynamically_typed_param", rclcpp::ParameterValue{}, descriptor);
有关详细信息,请参阅 https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/galactic/rclcpp/doc/notes_on_statically_typed_parameters.md.
用于检查 QoS 配置文件兼容性的新 API
qos_check_compatible 是一个用于检查两个 QoS 配置文件兼容性的新功能。
Related PR: ros2/rclcpp#1554
rclpy
删除已弃用的 Node.set_parameters_callback
方法 Node.set_parameters_callback 在 ROS Foxy <https://github.com/ros2/rclpy/pull/504>`_ 中已弃用,并已在 ROS Galactic 中被删除。
请改用 Node.add_on_set_parameters_callback()。
以下是使用它的一些示例代码。
import rclpy
import rclpy.node
from rcl_interfaces.msg import ParameterType
from rcl_interfaces.msg import SetParametersResult
rclpy.init()
node = rclpy.node.Node('callback_example')
node.declare_parameter('my_param', 'initial value')
def on_parameter_event(parameter_list):
for parameter in parameter_list:
node.get_logger().info(f'Got {parameter.name}={parameter.value}')
return SetParametersResult(successful=True)
node.add_on_set_parameters_callback(on_parameter_event)
rclpy.spin(node)
运行此命令来查看参数回调的实际效果。
ros2 param set /callback_example my_param "Hello World"
参数类型现在默认为静态
在 Foxy 及更早版本中,设置参数的调用可能会更改其类型。 从 Galactic 开始,参数类型是静态的,默认情况下无法更改。 如果需要以前的行为,则在参数描述符中将“dynamic_typing”设置为 true。 这是一个例子。
import rclpy
import rclpy.node
from rcl_interfaces.msg import ParameterDescriptor
rclpy.init()
node = rclpy.node.Node('static_param_example')
node.declare_parameter('static_param', 'initial value')
node.declare_parameter('dynamic_param', 'initial value', descriptor=ParameterDescriptor(dynamic_typing=True))
rclpy.spin(node)
运行这些命令来查看静态和动态类型参数有何不同。
$ ros2 param set /static_param_example dynamic_param 42
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /static_param_example static_param 42
Setting parameter failed: Wrong parameter type, expected 'Type.STRING' got 'Type.INTEGER'
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/galactic/rclcpp/doc/notes_on_statically_typed_parameters.md。
用于检查 QoS 配置文件兼容性的新 API
rclpy.qos.qos_check_compatible is a new function 用于检查两个 QoS 配置文件的兼容性。
如果配置文件兼容,则使用它们的发布者和订阅者将能够相互通信。
import rclpy.qos
publisher_profile = rclpy.qos.qos_profile_sensor_data
subscription_profile = rclpy.qos.qos_profile_parameter_events
print(rclpy.qos.qos_check_compatible(publisher_profile, subscription_profile))
$ python3 qos_check_compatible_example.py
(QoSCompatibility.ERROR, 'ERROR: Best effort publisher and reliable subscription;')
rclcpp_action
操作客户端目标响应回调签名已更改 “”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”
目标响应回调现在应将共享指针指向目标句柄,而不是未来。
For example, old signature:
void goal_response_callback(std::shared_future<GoalHandleFibonacci::SharedPtr> future)
新签名:
void goal_response_callback(GoalHandleFibonacci::SharedPtr goal_handle)
Related PR: ros2/rclcpp#1311
rosidl_typesupport_introspection_c
从数组中获取元素的函数中的 API 中断
该函数的签名已更改,因为它在语义上与用于从数组或序列中获取元素的所有其他函数不同。
这仅影响使用自省 typesupport 的 rmw 实现的作者。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 ros2/rosidl#531。
rcl_lifecycle 和 rclcpp_lifecycle
RCL 的生命周期状态机获得新的 init API
rcl_lifecycle 中的生命周期状态机经过修改,需要新引入的选项结构,结合状态机的一般配置。 选项结构允许指示状态机是否应使用默认值初始化,其附加服务是否处于活动状态以及要使用哪个分配器。
rcl_ret_t
rcl_lifecycle_state_machine_init(
rcl_lifecycle_state_machine_t * state_machine,
rcl_node_t * node_handle,
const rosidl_message_type_support_t * ts_pub_notify,
const rosidl_service_type_support_t * ts_srv_change_state,
const rosidl_service_type_support_t * ts_srv_get_state,
const rosidl_service_type_support_t * ts_srv_get_available_states,
const rosidl_service_type_support_t * ts_srv_get_available_transitions,
const rosidl_service_type_support_t * ts_srv_get_transition_graph,
const rcl_lifecycle_state_machine_options_t * state_machine_options);
RCL 的生命周期状态机存储分配器实例
选项结构(如上所述)包含用于初始化状态机的分配器实例。 此选项结构及其体现的分配器存储在生命周期状态机中。 直接的结果是,“rcl_lifecycle_fini 函数”不再需要其 fini 函数中的分配器,而是使用选项结构中的分配器集来释放其内部数据结构。
rcl_ret_t
rcl_lifecycle_state_machine_fini(
rcl_lifecycle_state_machine_t * state_machine,
rcl_node_t * node_handle);
RCLCPP 的生命周期节点公开了不实例化服务的选项
为了使用 rclcpp 的生命周期节点而不公开其内部服务(例如 change_state、get_state 等),生命周期节点的构造函数有一个新引入的参数,指示服务是否可用。
此布尔标志默认设置为 true,如果不希望,则不需要对现有 API 进行任何更改。
explicit LifecycleNode(
const std::string & node_name,
const rclcpp::NodeOptions & options = rclcpp::NodeOptions(),
bool enable_communication_interface = true);
Related PRs: ros2/rcl#882 and ros2/rclcpp#1507
rcl_lifecycle 和 rclcpp_lifecycle
记录 - 按时间分割
已知问题
ros2cli
守护进程减慢 Windows 上的 CLI 速度
作为一种解决方法,可以在没有守护进程的情况下使用 CLI 命令,例如:
ros2 topic list --no-daemon
问题由 ros2/ros2cli#637.
rqt
一些 rqt_bag 图标缺失 “”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”
“rqt_bag”中缺少“放大”、“缩小”、“缩放主页”和“切换缩略图”图标。 该问题在 ros-visualization/rqt_bag#102 中进行了跟踪
大多数 rqt 实用程序在 Windows 上无法独立运行
在 Windows 上“独立”启动 rqt 实用程序(如 ros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph)通常不起作用。
解决方法是启动 rqt 容器进程(rqt),然后插入要使用的插件。
rviz2
RViz2 面板关闭按钮是空白 “”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”“”
每个 RViz2 面板的右上角都应包含一个“X”,以便用户关闭面板。 这些按钮确实存在,但所有平台上都缺少按钮内的“X”。 该问题正在 ros2/rviz2#692 中跟踪。
发布前的时间线
- Mon. March 22, 2021 - Alpha
Preliminary testing and stabilization of ROS Core [1] packages.
- Mon. April 5, 2021 - Freeze
API and feature freeze for ROS Core [1] packages in Rolling Ridley. Note that this includes
rmw, which is a recursive dependency ofros_core. Only bug fix releases should be made after this point. New packages can be released independently.- Mon. April 19, 2021 - Branch
Branch from Rolling Ridley.
rosdistrois reopened for Rolling PRs for ROS Core [1] packages. Galactic development shifts fromros-rolling-*packages toros-galactic-*packages.- Mon. April 26, 2021 - Beta
Updated releases of ROS Desktop [2] packages available. Call for general testing.
- Mon. May 17, 2021 - RC
- Release Candidate packages are built.
Updated releases of ROS Desktop [2] packages available.
- Thu. May 20, 2021 - Distro Freeze
Freeze rosdistro. No PRs for Galactic on the
rosdistrorepo will be merged (reopens after the release announcement).- Sun. May 23, 2021 - General Availability
- Release announcement.
rosdistrois reopened for Galactic PRs.